1 Introduction
With the development of banking industry, large-scale commercial banks are getting bigger, and small-sized banks must survive in a gap. We are trying to help our client, the Portuguese Bank, which is a small-sized bank, to capture the right target customers to increase deposit account sign-up rate to increase revenue. We have the data of customers from its last campaign, our goal is to analyze the data, and trying to figure out the customers’ categorizing pattern and the possibilities of a customer signing up the deposit account with our client. Once we get the result from our analysis model from the data, we can help the Portuguese Bank make target customer oriented marketing and advertising strategies, and utilize its limited resources to achieve expected outcome.
2 Data Description
The data is from UCI (http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Bank+Marketing) and it is related with direct marketing campaigns of a Portuguese banking institution. The marketing campaigns were based on phone calls.

There are total of 45211 record instances and 21 variables. We created an Excel sheet to explain all the variables as follow:

Y is our target variable which describes whether that client subscribed a deposit after the campaign. We deleted the entire social and economic context variables (variable 16 to variable 20) because they have quite low relevancy with the target variable and our model in this case.
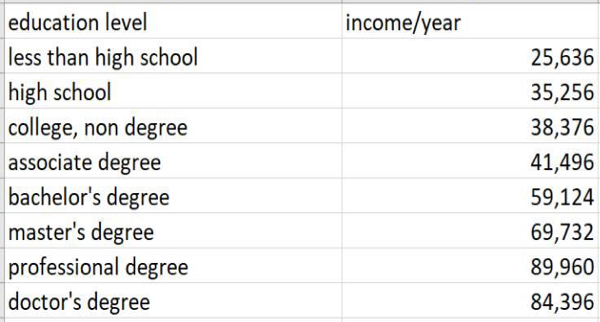
We decided to merge the data of average income by education level in the US into our dataset. Merging data is from Smartasset.com and the link is as follow: https://smartasset.com/retirement/the-average-salary-by-education-level Basically, there are four categories of education: primary, secondary, ternary and unknown. And correspondingly there are four average annual income levels: $25,636.00, $36,816.00, $68,941.60 and unknown. Following is a sample screenshot of the merged dataset.

3 Problem Statement
We are trying to find a way to improve the effectiveness of the campaign. And we decided to use decision tree model and K-means cluster model to figure out who are more likely to open a deposit account in the bank. Decision tree model is utilized to find a rule to predict how likely a customer would open an account in the bank. And K-means cluster model is utilized to see the cluster patterns to categories customers.
By developing these two models, we can help the bank to better utilize its source on marketing and advertising to increase revenue.
4 Methodology
4.1 Model 1: Decision Tree
Data Collection
The main dataset was from UCI, and the merging data was from Assetsmart.com which are mentioned in the data description part.
Data Preprocessing
First, we merged two datasets together by R program. As the second dataset has 9 education levels (see table below) but the attribute Education in the main dataset only has 4, we merged these 9 education levels into 4 levels (Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Unknown). The primary level is less than high school. The secondary level is high school and college, non-degree. The tertiary level is associate degree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, professional degree and doctor’s degree. The average income for these 4 levels are the sum-average of the classified 9 levels.
Variable Selection
Firstly, we input all the attributes to build a decision tree and have a result below:
From the result above, we found the data may not suitable for a decision tree model. Then we tried to figure out if there were some useful association rules and if we can filter some good features for decision tree.
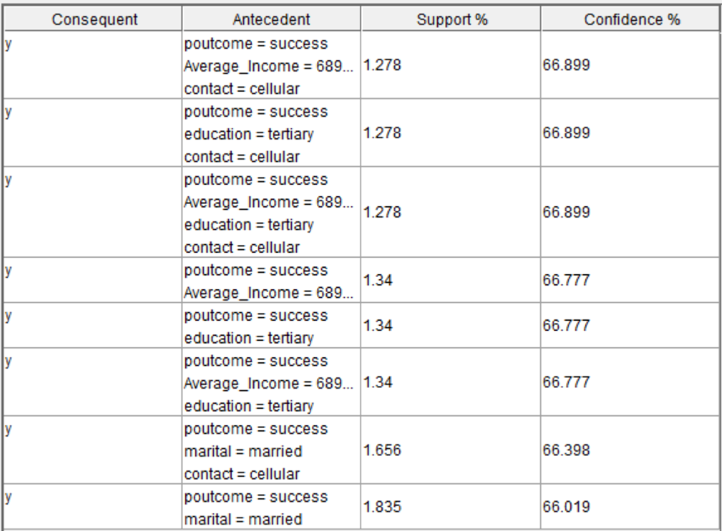
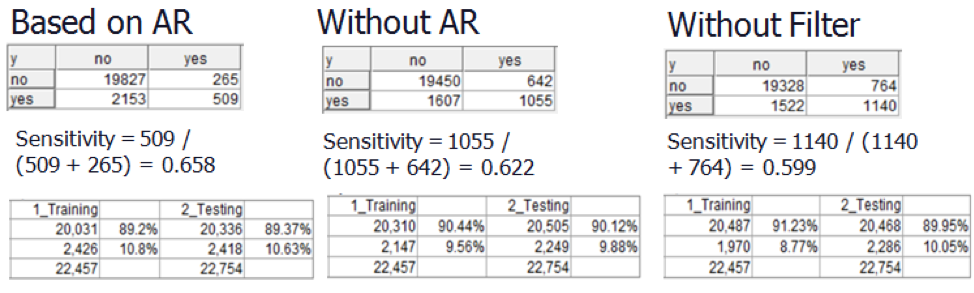
For decision tree model, attribute ‘y’ is the target. As there were lots of attributes, we had to decide which attributes are more influential to the model. So, we used two methods to filter the attributes. The first method was association rule. We used association rule to define which attributes are important to the model (See table below). Then we used filter node to remove other attributes and did the decision tree model by using these attributes which are in the table below. After filtering the attributes, the sensitivity rate was higher than the original one, and the accuracy was almost same which means association rule worked well in this case.
The second method is using the attributes which are important in the original decision tree model and remove other attributes.
Model Building
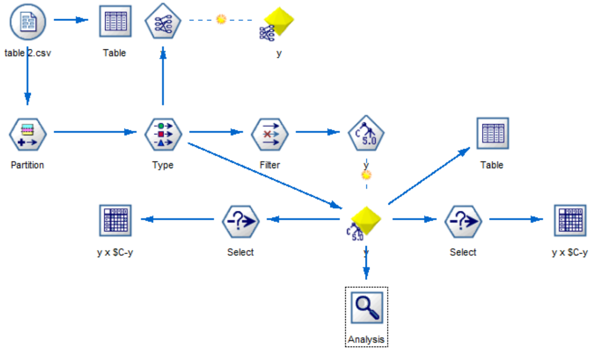
We used SPSS to build our model and we set two datasets, training and testing, 50% for each, to check accuracy of our model. Then, we used C 5.0 to do decision tree model and used Analysis node to check other information.
Evaluation
For decision tree model, first we had to test whether the model works well. The sensitivity in training is 0.636 and the sensitivity in testing is 0.658 which means the model worked out well. Then, the decision tree outcome showed that ‘Poutcome’ is the most important and the only attribute that predicts the result. Any other attributes would make the outcome worse. Besides, the rate of people who said ‘yes’ in the population is 0.117. After doing the decision tree, we can locate the target population and the rate of people who said ‘yes’ in the target population is 0.658. It’s 5.6 times of original which means the decision tree model really helped to locate the target customers. Besides, comparing two filter method, we can see that the accuracy were almost the same but the model has the highest sensitivity by using association rule method(See table below). So, association rule is the better method to filter attributes.
Model 2: K-Means Cluster
Data Preprocessing
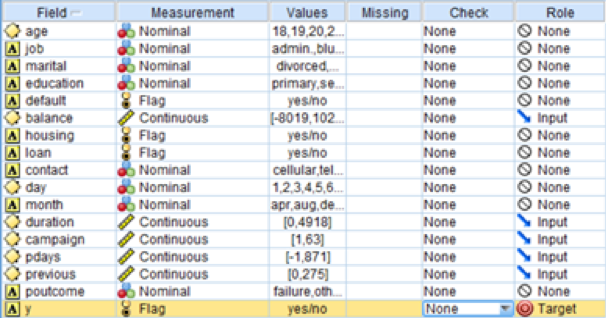
For the first clustering, we used the same data in the decision tree model. For the second clustering, we used the data without the ones that was predicted as “yes” by decision tree. For feature selection, we selected the features for K clusters by the logic reason. K cluster is a method to cluster the data by their continuous features, so we deleted the features that are not continuous, such as nominal, binormal.
Model Building
We did K-means twice. The first time, we used the original data to see if K-means cluster worked well. The second time, we used the new data which excluded 1511 instances that the decision tree predicted as “yes” to see if K-means cluster can be used with decision tree.
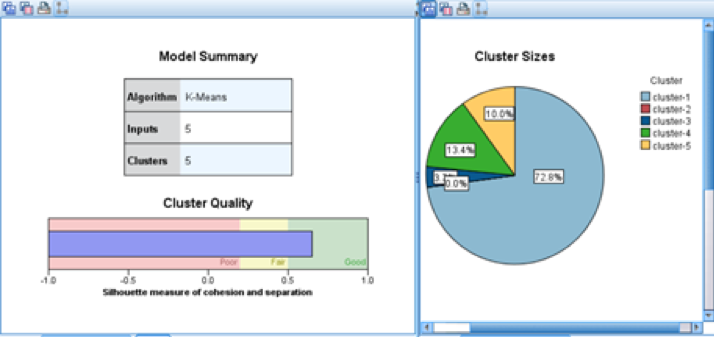
For these two processes, we used the same model with the same features and made 5 clusters. Clustering Model 1:
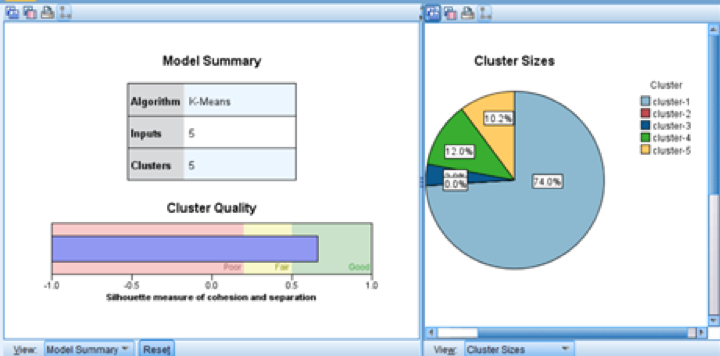
Clustering Model 2:
Firstly, we filtered the features we need:
Then we used K-means model and set number of clusters as 5. (cluster model 1)
(cluster model 2)
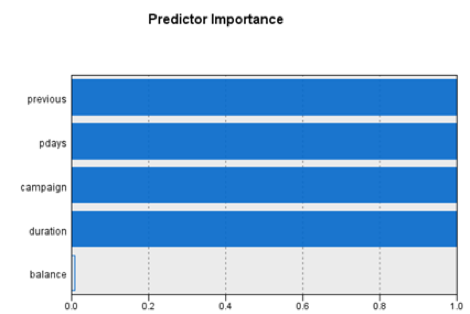
The two times cluster have the same predictor importance and almost the same clusters. (cluster model 1)
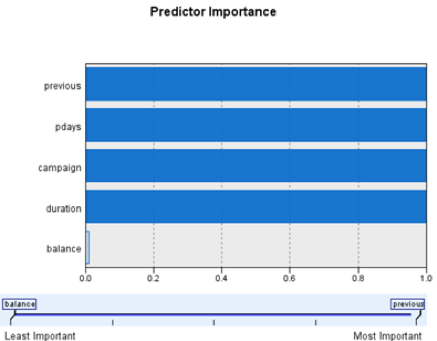
(cluster model 2)
(cluster model 1)
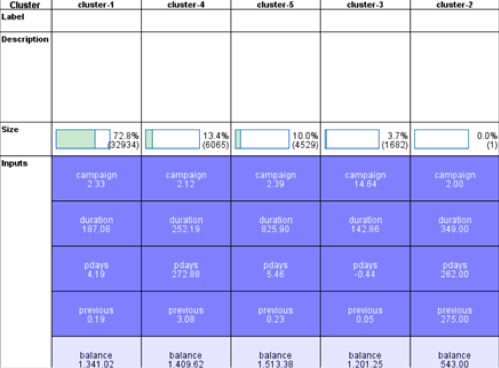
(cluster model 2)
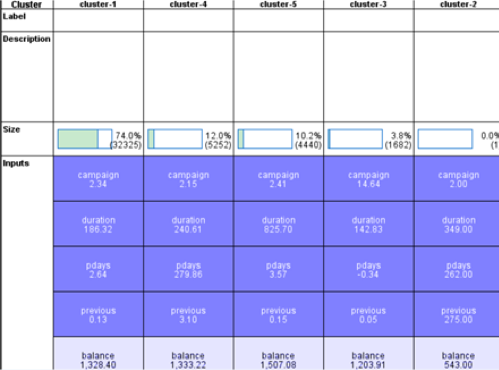
From the input figures above, we can see that for the two-time clusters only pdays have changed, the others are almost the same.
Evaluation
(cluster model 1)
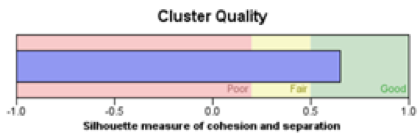
(cluster model 2)
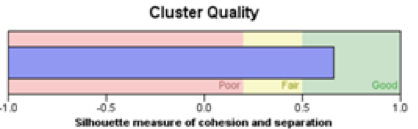
For this two clustering model, the cluster quality both located in the range of good quality, which means we have a good cluster.
From the proportion of the cluster results, we can see that cluster-5 contain the most proportion of our potential customers. So, we found a good cluster that contain more customers who would open a deposit account in the bank. The bank can focus more on the customers in cluster 5 to improve the promotion effect.
From the input figures above, we can see that people in cluster 5 have a more duration time (which is the most distinctive), more but not too much campaign is useful and most balance is good. This is reasonable, for example, people spend more time to know something about the bank indicates that they are more willing to open an account and this is what duration reflects. (cluster model 1)
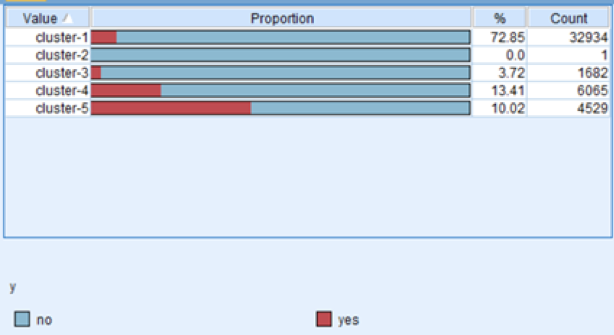
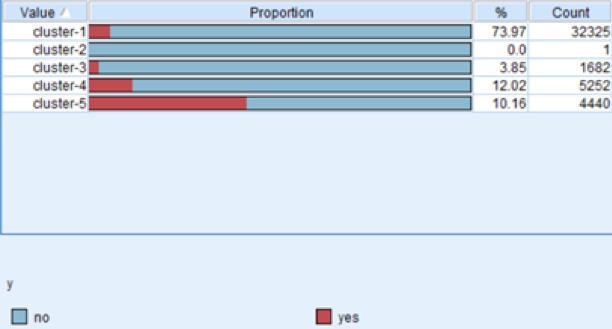
And After we deleted the 1511 instances that the decision tree predicted as “yes”, we found the deleted “yes” instances are mostly from cluster 1 and cluster 4. As for cluster 5, it doesn’t affect much, which means we can combine decision tree and K-means cluster focusing on the predicted “yes” customers and cluster-5 customers to improve the campaign efficiency. (cluster model 2)
5 Result & Conclusion
5.1 Analysis Aspect
About 11% of the customers said “yes” from the original dataset, after the decision tree model, we found about 65% of the customers are very likely to say “yes” within the target customers group. Besides, the attribute ‘Poutcome’ is the only factor that influence the outcome. Customers who have opened account in the past are very likely to stay with the bank. Any other attributes would make the outcome worse. For those in the targeted customers group who said “no”, K-means clustering told us customers in cluster 5 are more likely to be influenced by the campaign and change their mind to say “yes” to the bank deposit account.
5.2 Business Aspect
From the analysis, we have several business suggestions for our client:
- Focus on the customers who have had business with the bank before, they are likely to stay with the bank.
- Customers who attended the campaign for 2 to 3 times and spent more time on the phone during last campaign is very likely to open a deposit account. Take them as priori customers.
- Customers who have stable cash balance is more likely to deposit their money in the bank.
- 3 to 5 days after the campaign is the best time to follow up the customers.